GIMP Image Editor: How to edit images into PGM ?
- GIMP: GNU Image Manipulation Program.
- GIMP Image Editor is a Free and Open Source Image Editor. click here to download and install.
- It is used for converting images into a PGM Extension.
Different Type of Image Extension:
JPEG -> Joint Photographic Experts Group
PNG -> Portable Network Graphics
XCF -> eXperimental Computing Facility
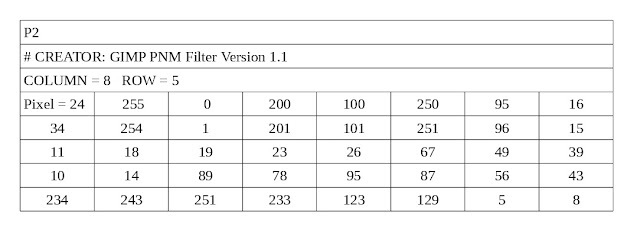
PGM -> Portable Gray Map
-> In image processing technique, we have to take input as an image. So, the most efficient extension for input image is the ".PGM" extension image.
-> The ".pgm" extensible Images are editable in a text editor.
-> The ".xcf, .png, .jpeg" extensible images are not editable in a text editor.
-> ASCII: American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
Process of Converting Images into a PGM Image:
-> Download the GIMP File -> Install.
-> Download image -> Save Download Image -> "Right Click" on saving image -> go to "Open with" and -> click on "GIMP Image Editor" -> Go to the "file" in open image -> Click on "save as..." -> Go to top and Change the Name: of the file extension into "pgm" -> Go to right bottom corner, click "Save" -> Click "Take me to the Export dialog" -> Go to Right bottom corner and click "Export" -> Choose "ASCII" -> Export.
.png)